Volcano Watch: Voggy skies from days gone by — reviewing Kilauea’s gas release
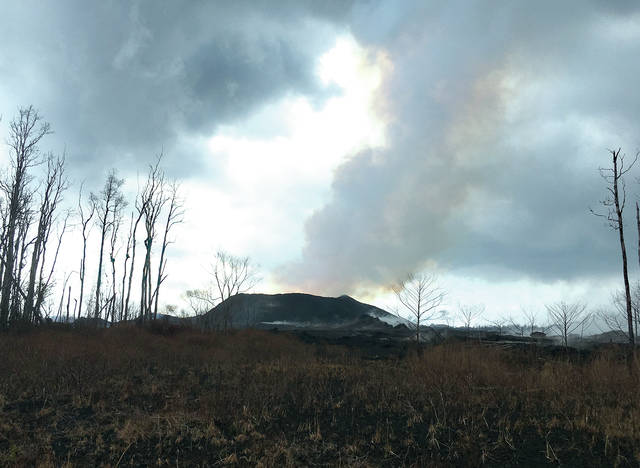

T. ELIAS/US Geological Survey photo
In mid-July, fissure 8 on Kilauea volcano’s lower East Rift Zone was emitting more than 50,000 tons of sulfur dioxide gas per day, creating high levels of vog on the island. Since early August, lower East Rift Zone SO2 emissions have dropped to less than 100 tons per day, resulting in better air quality for Hawaii.
Many Hawaii Island residents are familiar with the volcanic air pollution known as vog. The main culprit in the formation of vog is sulfur dioxide gas released from Kilauea’s eruptions (see vog.ivhhn.org/what-vog for more information).
Many Hawaii Island residents are familiar with the volcanic air pollution known as vog. The main culprit in the formation of vog is sulfur dioxide gas released from Kilauea’s eruptions (see vog.ivhhn.org/what-vog for more information).
Vog watchers might have noticed significant changes in air quality on the island since early May, when Kilauea’s extraordinary lower East Rift Zone eruption began. Revisiting how much SO2 has been released from Kilauea during the past decades helps us understand the island’s current vog situation.
ADVERTISING
Since the amount and location of SO2 release from Kilauea has changed with time, the concentration and distribution of vog on the island also has changed.
Some residents might recollect clear skies in leeward Hawaii prior to 1986. During that period, Kilauea’s summit was the focus of gas release, emitting just a few hundred tons of SO2 each day, which primarily impacted areas near the volcano’s summit.
In 1983, Kilauea’s East Rift Zone eruption at Pu‘u ‘O‘o began, with episodic high lava fountains. During the fountaining, large amounts of SO2 gas (up to 30,000 tons) were released during a period of about a day, but only about once a month.
Prevailing trade winds cleared the air between episodes.
A few years later, the volcanic activity abruptly changed to nearly continuous eruption of lava and gas, with about 2,000 tons of SO2 released daily. The continuous gas release provided little opportunity for the air to clear, and vog became a common feature for leeward Hawaii, where the trade winds blew the emissions.
In 2008, SO2 emissions from Kilauea, and vog on the island, increased significantly with the opening of the summit crater within Halema‘uma‘u, which hosted a lava lake for the next decade.
During the past several years, summit SO2 emissions averaged about 5,000 tons per day while Pu‘u ‘O‘o emissions progressively declined to less than a few hundred tons per day.
The total gas release from Kilauea in recent years (until early May of this year) was about 2.5 times those measured prior to 2008.
This May, significant changes in gas release accompanied the collapse events at Kilauea’s summit and the LERZ eruption. These changes were even greater in magnitude than past changes.
At the summit, ash-rich explosions in May produced SO2 emissions that peaked near 10,000 tons per day. Since then, as summit activity evolved into less explosive collapse events, SO2 emission rates have steadily declined.
The latest measurements indicate summit emissions are now only a few hundred tons per day, a rollback to pre-2008 summit emission rates.
At Pu‘u ‘O‘o, SO2 emissions have rarely risen above a few hundred tons per day since May, a situation that continues as of this writing.
Along the LERZ, the 24 fissures that erupted lava in and near Leilani Estates released massive amounts of SO2. Emissions in early May were similar to the long-term average emissions from Kilauea’s summit lava lake. But as lava effusion became more focused at fissure 8, LERZ SO2 emission rates progressively increased.
By early June, LERZ measurements indicated emission rates upward of 50,000 tons per day. These high levels persisted until early August.
Sustained release of SO2 at such a high magnitude is unprecedented in Kilauea’s history of SO2 emission rate measurements, which began in the late 1970s.
When lava output from fissure 8 suddenly declined in early August, SO2 emission rates dropped precipitously as well. Emissions on Aug. 3 indicated tens of thousands of tons of SO2 coming from the fissure 8 vent, but just two days later, on Aug. 5, the emission rate was only about 200 tons per day.
Since then, SO2 has further declined.
With the LERZ emitting less than 100 tons per day, and Pu‘u ‘O‘o and the summit each emitting only a few hundred tons per day, the current SO2 emissions from all Kilauea sources total well less than 1,000 tons per day.
This is the lowest overall SO2 emission rate in more than a decade.
Low SO2 emissions mean better air quality for Hawaii. While it’s not yet clear if the LERZ eruption is pau or paused, it’s worth taking a deep breath and enjoying the lowest SO2 emission rates from Kilauea in a long time.
Volcano activity updates
Activity on Kilauea’s lower East Rift Zone and at the summit of the volcano remain greatly diminished as of Aug. 23.
LERZ activity was limited to only a few ocean entries oozing lava and producing minimal laze plumes. Seismicity and ground deformation were negligible at the summit of Kilauea, with no collapse event since Aug. 2. However, hazardous conditions remain in both areas.
Residents in the lower Puna and Kilauea summit areas should stay informed and heed Hawaii County Civil Defense closures, warnings and messages (http://www.hawaiicounty.gov/active-alerts). HVO daily status reports are posted at https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/volcanoes/kilauea/status.html.
At Mauna Loa, HVO geophysical monitoring networks indicate earthquakes and deformation are near background levels, and the USGS Volcano Alert level for the volcano remains at Normal.
HVO continues to closely monitor Kilauea and Mauna Loa and will report any significant changes on either volcano.
No earthquakes were reported felt in Hawaii this past week.
Visit HVO’s website (https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/hvo) for past Volcano Watch articles, Kilauea daily eruption updates, Mauna Loa monthly updates, volcano photos, maps, recent earthquake info, and more. Email questions to askHVO@usgs.gov.
Volcano Watch (https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/hvo/hvo_volcano_watch.html) is a weekly article and activity update written by U.S. Geological Survey Hawaiian Volcano Observatory scientists and affiliates.